What it actually means if one of your fingers turns white when it’s cold
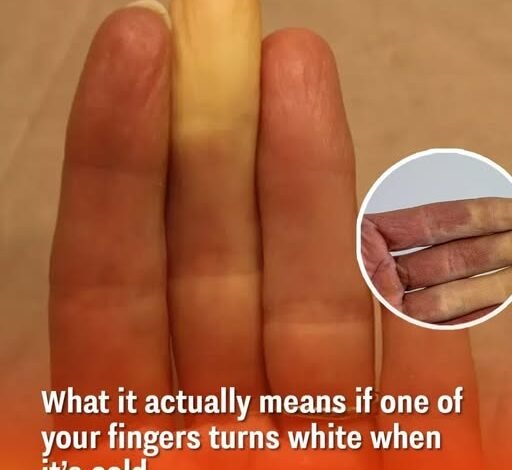
Raynaud’s phenomenon is a condition where blood vessels in the extremities constrict in response to cold or stress, reducing blood flow and causing temporary color changes. It primarily affects fingers, toes, ears, nose, or nipples. This response is a natural reaction to protect the body, although it can lead to discomfort.
When exposed to cold or stress, the blood vessels narrow, limiting circulation. Initially, the affected area may turn white or pale due to reduced blood flow. As oxygen levels drop, the skin can shift to blue or purple, and finally turn red when blood returns.
Common symptoms include numbness, coldness, tingling, and pain in the affected areas. Raynaud’s can be classified into two types: primary, which occurs without an underlying condition, and secondary, which is linked to diseases like lupus or scleroderma. Each type may require different management approaches.
To manage Raynaud’s, it is important to keep warm, avoid stress, and make lifestyle changes. In severe cases, medical treatment options may be necessary. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized medical advice.